:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(jpeg)/Health-GettyImages-2170250544-bd49d2b0941f45c281a2f4dbd08fbaa9.jpg)
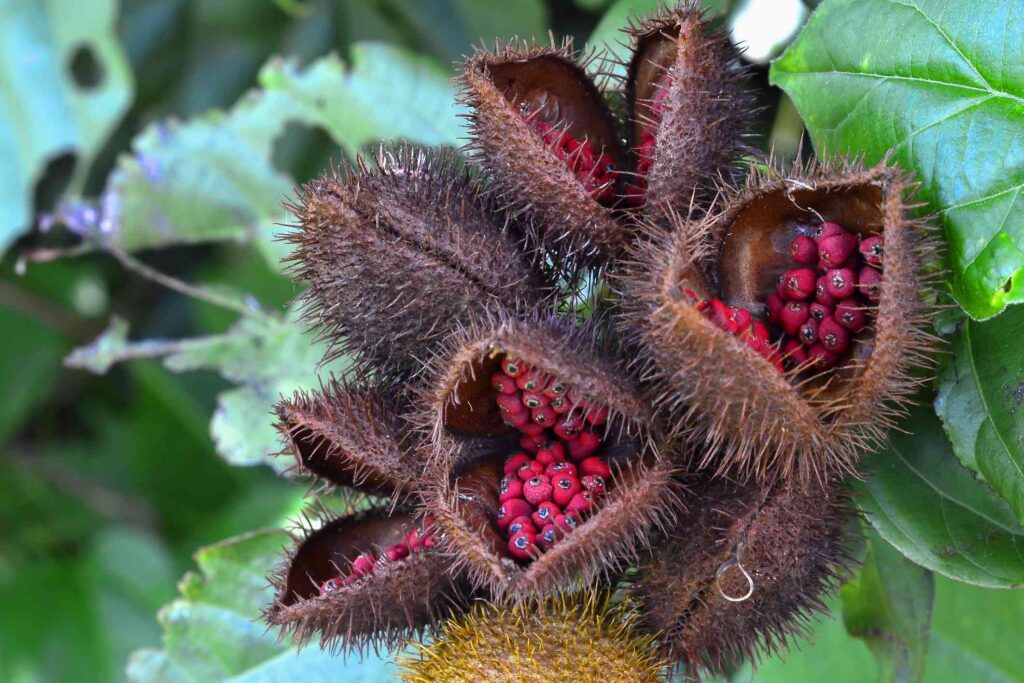
Annatto (Bixa orellana), also known as achiote, urucum, and bija, is a small shrub or tree native to Central and South America. It is primarily grown for its vibrant reddish-orange seeds, which are used as a natural food coloring in various products.
Traditionally, annatto is used to prevent and treat heartburn, chest pain, fevers, and diarrhea. It can also be used to treat skin conditions and some infectious diseases.
Modern science has just begun to uncover the health effects of annatto. They include benefits like slowing the growth of disease-causing bacteria, improving heart function, and relieving muscle pain and soreness, among others.
Annatto is a natural source of antioxidants, which help protect your cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. When free radicals build up in your cells, they can cause oxidative stress, which is linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
The two main antioxidants in annatto are bixin and norbixin, which are plant pigments that give the seeds their distinctive red-orange color. Laboratory studies show that annatto seed extracts containing these pigments show strong antioxidant activity. This means they can help fight cell-damaging free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress.
More human studies are necessary to verify these findings.
Annatto is rich in several key antimicrobial compounds, which can limit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and parasites. These include flavonoids, polyphenols, tannins, quinones, terpenoids, and alkaloids. Therefore, these compounds may help fight various pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria and fungi.
Extracts from the plant’s leaves, seeds, and roots significantly inhibit the growth of diarrhea-inducing bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus (staph), Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Shigella dysenteriae (dysentery).
Annatto may also be effective against fungal infections caused by Candida utilis, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger.
The studies behind these potential benefits used different extraction methods to obtain annatto, leading to varying results. As such, more research is needed to fully understand the antimicrobial benefits of annatto extracts.
Annatto contains a unique form of vitamin E known as tocotrienols, which may boost your heart health.
One study examined the effects of combining a heart-healthy diet with daily doses of annatto tocotrienol, ranging from 125-750 milligrams, on 31 individuals with high cholesterol. The results showed that after four weeks, a low dose of 250 milligrams led to a significant reduction in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
The same study also found that the annatto supplement helped reduce several inflammatory markers associated with cardiovascular disease, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. The researchers believe these effects are due, in part, to the anti-inflammatory properties of tocotrienols. Still, more research is required to validate these results.
Emerging research suggests that the tocotrienols in annatto may also preserve bone health.
A preliminary study explored the effect of an annatto-derived tocotrienol supplement on several bone markers in postmenopausal women with osteopenia (low bone mineral density). The researchers found that the supplement decreased bone resorption (breakdown) and improved bone formation.
These effects may be due to tocotrienols’ ability to fight oxidative stress. As a result, the study indicates the potential of annatto tocotrienols to support bone density and strength.
Annatto may be a supportive herb for athletes and active individuals who want to manage muscle soreness and improve athletic performance.
In one study, young men who were given a supplement with a mixture of annatto and ginger powder experienced reduced muscle soreness following eccentric (lengthening) muscle contraction exercises.
Another study in male recreational runners found that combining annatto, ginger, and devil’s claw root helped reduce inflammatory knee pain. These benefits may be due to the antioxidant properties of the plants, though further research is needed to confirm these findings.
The fruit of the annatto tree has a reddish-brown, heart-shaped exterior that is covered in short, bristle-like hairs. As it ripens, the fruit splits open, revealing 30 to 60 reddish-orange seeds. These seeds are the source of a natural dye, spice, and paste used in a variety of foods, including:
- Butter
- Margarine
- Ice cream
- Processed cheese
- Condiments
- Sauces
- Soup
- Sausage
- Chicken
Annatto supplements are also available in liquid, powder, and capsule form with more concentrated doses of vitamin E tocotrienols. Some formulations of annatto are packaged with other nutrients and compounds, so it’s important to check the label.
Dosage
The studies that investigated the benefits of annatto tocotrienol supplements used doses between 125-750 milligrams.
However, there is currently no standardized dosage for annatto supplements. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dose based on your individual health needs.
Annatto seed extracts are generally considered safe when used as a natural food coloring and seasoning, with an acceptable daily intake of 2.5 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. Annatto leaf powder is likely safe when taken in doses of up to 750 milligrams daily for up to one year.
When consumed in safe amounts, annatto is usually well tolerated. However, in rare cases, annatto can cause constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) flare-ups, and allergic reactions. If you experience any of these symptoms, stop taking annatto and speak to your healthcare provider.
People who are pregnant or lactating should be cautious with annatto supplementation, as research is lacking regarding its safety in these populations.
Potential Drug Interactions
Annatto may interact with commonly prescribed medications and other supplements, including:
- Anti-diabetes drugs: Taking annatto with diabetes medications may reduce the effectiveness of the drug or increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Monitor blood glucose levels closely when taking these two together.
- Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) substrates: Annatto might increase the body’s metabolism of these drugs. This can lead to a faster breakdown of these medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
- Herbs that lower blood sugar: Some studies indicate that taking annatto extract with certain herbs, such as bitter melon, ginger, fenugreek, and willow bark, may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
If you’re taking one or more of these drugs or herbal remedies, consult your healthcare provider to discuss potential interactions.
Can You Take Too Much Annatto?
Currently, there isn’t enough reliable evidence to determine if large doses of annatto are safe or harmful. Always check the supplement facts label and follow the dosing instructions outlined by the manufacturer or your healthcare provider to avoid consuming large amounts.
In the rare event that an allergic reaction to annatto occurs, symptoms may include:
- Hives
- Swelling of the face, lips, or mouth
- Severe hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Anaphylaxis (severe, body-wide allergic reaction)
These symptoms may occur due to traces of seed protein in annatto food coloring. If you experience an allergic reaction, seek medical attention immediately and avoid consuming products containing annatto in the future.
Annatto food coloring may also increase the following symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in susceptible individuals.
To improve these symptoms, avoid all foods and supplements that have annatto listed in the ingredients.
Annatto is a small shrub or tree with bright, reddish-orange seeds that are commonly used as a natural food coloring agent and condiment.
The seeds contain beneficial compounds, such as bixin, norbixin, and tocotrienols, that have been shown to reduce cell-damaging free radicals, fight pathogens, lower cholesterol, improve bone health, and reduce muscle soreness. However, further research needs to be done to confirm these effects and better understand the underlying mechanisms involved.
Annatto supplements are available in liquid, powder, and capsule form. Before taking an annatto supplement, speak with your healthcare provider about the appropriate dosage, potential drug interaction, and possible side effects.